Depending on your professional activity, you will have to use work shoes, protection Where of security. The former, cataloged under the EN ISO 20347 standard, are not protected by a safety cap and are suitable for restorative, medical or service trades. Protective and safety shoes are they fitted with a impact resistant toe cap, respectively, of 100 and 200 joules. That is to say, they can withstand the fall of a 10 kg object dropped at 1 m for the protective shoe, and the fall of a 20 kg object dropped at 1 m for the safety shoe.
Regarding the nomenclature EN ISO 20345, it encompasses all safety shoes and allows them to be distinguished according to their strengths, so that they can best meet the requirements of your professional environment. Today we are therefore going to help you choose the ideal shoe model to meet the requirements of your trade.
Main standards:
The main protective characteristics of a safety shoe are codified as follows:
B: Refers to theshoe tip 200 joules impact resistant. it’s about the fundamental property so that a shoe can claim the term of Safety shoe. The end cap can be in steel or aluminum, or in composite materials (polycarbonate, glass fibers, carbon fibers) if the workplace requires a metal-free alternative.
A: Defines the character antistatic. Such a shoe makes it possible to avoid the accumulation of static electricity and evacuate it towards the ground. This is an essential property in the presence of material to electronic components.
![]()
FO: Attests to the shoe resistance to hydrocarbons. A FO certified sole, in contact with such materials, undergoes deformation and an increase in volume much less than a conventional sole.
![]()
E: Indicates the performance ofenergy absorption in the heel. A standardized heel must be able to withstand a pressure of 20 joules.
![]()
WRU and WR: Concerning the capacities of resistance to water penetration. A WRU shoe provides protection to the upper of the shoe, while a WR shoe acts to slow the intrusion of water on the whole of the shoe. The latter is therefore particularly recommended for highly humid environments.
![]()
P: Distinguishes the ability of a shoe to measure itself against risks of penetrating objects metallic or not. On construction sites or in industrial trades, this characteristic is one of the most important for the safety of the carrier.

Gliding standards:
![]()
After the protective cap, this is the second essential property so that a shoe can be classified as Safety shoe. It determines the adhesion capacity on certain types of smooth floors. There are two categories:
– MS : The shoe grips the ceramic floors. It supports an inclination of up to 7 ° under the pressure of a force of 500 N (the equivalent of the pressure of human walking). It is also resistant to slipping in contact with cleaning products or detergents. soapy type.
– SERB : Under the same test conditions, the shoe is this time designed to adhere to steel floors can be covered with oily matter.
When a shoe meets the criteria of two categories, it is assigned to the class named SRC. In order for a shoe to be categorized as a safety shoe, it must comply with the requirements of the SRA, SRB, or both (SRC) standard.
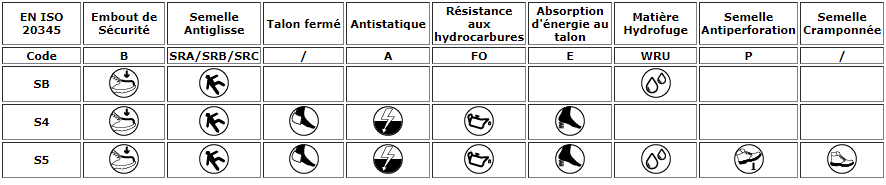
Classes of safety footwear:
Thanks to the aforementioned standards, it is now possible to catalog safety footwear under different classes which each provide a certain level of protection. Low shoes are stored as follows:
– SB: The basic safety shoe that holds the fundamental protections. That is to say a tip of standard B resistant to a force of 200 joules, as well as a capacity of slip resistance of SRA, SRB or SRC standard. (In addition, the SB high shoes have the same protections and are also water resistant)
– S1: The same requirements as the SB shoe, to which we add a closed heel, a resistance antistatic A, performance ofheel absorption E and a contact resistance to hydrocarbons. (About S4 high shoes, they have the same characteristics)
– S1P: Similar to S1, but which additionally has a puncture resistance P. The S1P shoes suitable for dry or indoor environments. They thus adapt to crafts, light industry or logistics.
– S2: The shoe has the same characteristics as S1, with the addition of a resistance to water penetration WRU. It can therefore meet the needs of the catering industry or the food industry.
– S3: Fulfills all the requirements of S2 and is complemented by a puncture resistance P and has walking crampons on the sole. Most complete class which is highly suitable for work in construction, heavy industry or green spaces. (S5 high shoes have the same properties)

Additional standards:
In addition to these classes, a safety shoe can benefit from additional standards providing specific benefits and protections recommended for certain types of trades.
– AN: The malleoli are a fragile part of the ankle. A shoe under this standard bring a additional protection at this level of the foot.
– M: The metatarsals, bones of the foot located between the heel and the phalanges of the toes, benefit from a additional protection under this standard.
– CI: This standard proposes a thermal insulation against the cold. The public works and green spaces professions are the most likely to find this asset essential in winter conditions.
– HI: Refers to a thermal insulation against continuous heat, such as summer work on roads or railroad ballast.
– HRO: One HRO shoe is resistance to heat contact on the outsole up to 300 °. It is therefore an essential ally when we are in contact with hot or molten metals.
– CR: This requirement meets the needs of cut resistance.

The safety shoes can, as we have just seen, cover the needs of many trades, ranging from catering to heavy industry. It is important to differentiate the strengths of each class and the attributes of additional standards, in order to best choose the pair of shoes that will suit your professional requirements. If work or protective footwear is not enough to ensure a safe working environment, the different types of safety footwear will certainly be able to perform the functions you need.
Class 1 : Safety shoes with the following characteristics are only intended for low shoes. 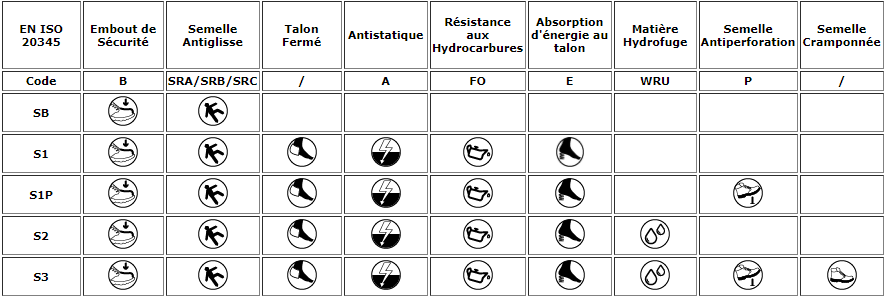
Class 2 : Safety shoes with the following characteristics are only suitable high shoes.